|
Mites are ectoparasites which means they are on the outside of the body. There are many different types of mites that can infest your cat or dog.
Ear Mites
Otodectes cynotis is commonly known as the ear mite, but it can also inhabit the skin of dogs and cats. When in the ears, these mites cause intense itching and accumulation of a dark brown to black, waxy or crusty exudate in the ear canals. There can be hair loss, head shaking, and trauma to the ears and head from scratching. When on the skin, especially the neck, rump, or tail, there is extreme itching, crusting, and possible hair loss.
 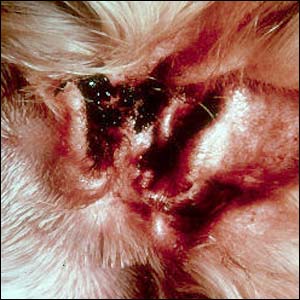
Click on the image below to see mites in the ear canal.
Ear mites are treatable. It is a contagious mite and all in-contact dogs and cats must be treated.
Skin Mites (Mange)
Demodectic mange is caused by the Demodex mite and there are different species for dogs and cats.
Demodex canis (pictured below on the left) is the most common mange mite of dogs. There are 2 other species of Demodex which are uncommon: a long-bodied mite (D. injai) and a short-bodied mite (unnamed). Demodex is not considered to be contagious or zoonotic. D. canis is a normal resident of dog skin and is present in small numbers on the skin of most healthy dogs. Transmission occurs from bitch to pups in the first couple of days of life.
There are 2 age presentations of demodicosis. Juvenile demodicosis occurs in young dogs typically 3 to 18 months of age. These dogs may have localized demodicosis or generalized demodicosis in which there are more than 5 lesions or 2 or more body areas that are affected. Adult-onset generalized demodicosis occurs in dogs older than 18 months of age and is typically associated with internal disease or immunosuppression (Cushing's disease, Addison's disease, hypothyroidism, cancer, immunosuppressive drug therapy). Typically there are patchy areas of hair loss, scaling, and itchiness. D. injai infestations can results in a greasy seborrhea with or without hair loss.
Demodicosis can be a genetic disease and affected individuals should not be bred. There are breed predispositions (dogs commonly affected): American Stafforsdshire terriers, American Pit Bull terriers, Boston terriers, Boxers, Afghan hounds, Chihuahuas, Collies, Dalmations, Doberman Pinschers, English bulldogs, German Shepherds, Great Danes, Old English Sheepdogs, Pugs, and Shar-Peis.
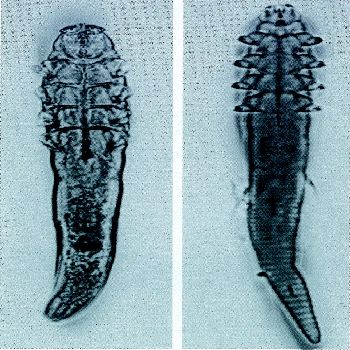
Demodex canis Demodex cati
Demodex cati (pictured above on the right) is a normal resident of cat skin, and Demodex gatoi is a contagious skin mite of cats. D. cati infections are typically associated with internal disease or immunosuppression (Feline leukemia virus, Feline Immunodeficiency virus, toxoplasmosis, lupus, cancer, or diabetes). Both mites cause extreme itching in cats which can be localized or generalized. The localized disease typically appears around the eyes, on the head, or on the neck. It can also cause extreme itching of the ears with a waxy exudate and possible hair loss or scaling or crusting on the ear. Generalized disease results in itchiness with or without hair loss, scaling, crusting, or redness and it is usually noted on the head, neck, limbs, flanks, or abdomen.
Treatment for dogs and cats can be challenging. Relapse/recurrence can occur. Spontaneous resolution of juvenile localized demodicosis in dogs can occur.
Scabies or sarcoptic mange is caused by different mites in dogs and cats.
Dog Scabies is caused by Sarcoptes scabiei variant canis, and it is a highly contagious and zoonotic parasite of dogs that can also infest humans and cats. This mite causes a sudden onset of intense itching. There can be crusting of the elbows, hocks, and ear margins.
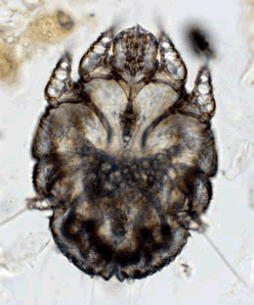 Sarcoptes scabiei variant canis Sarcoptes scabiei variant canis
All in-contact dogs and cats should be treated.
Cat Scabies
Cat Scabies is caused by Notoedres cati, and it is a highly contagious and zoonotic parasite of cats that can also infest dogs, humans, and rabbits. This mite causes a sudden onset of intense itching and dry, crusted lesions that first appear on the ear margins and spreads rapidly over the ears, head, face, and neck.

All in-contact dogs and cats should be treated.
Walking Dandruff
Cheyletiellosis, also known as walking dandruff, is a skin disease caused by Cheyletiella mites which live on hair and fur, but feed on the skin. It is a contagious and zoonotic disease and may infest dogs, humans, and cats. The most common symptom is excessive scaling (dandruff) and itching may also be seen.

All in-contact animals should be treated.
|




 Sarcoptes scabiei variant canis
Sarcoptes scabiei variant canis



